Posted by Ken Palmer on Mar 14th 2024
THCA vs. THC: What’s the Difference?
What is THCA?
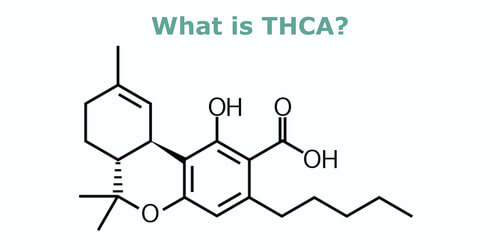
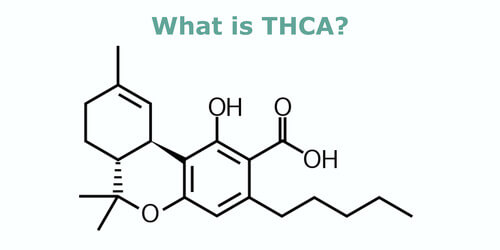
THCA stands for tetrahydrocannabinol-acid and is the molecule that is processed to become THC. Cannabinoid acids are common and prevalent in raw, untreated cannabis plants. The THCA cannabinoid is not psychoactive on its own and does not produce the same effects as THC when consumed.
Chemically, THCA molecules differ from THC molecules. They have carboxylic acid groups, which affect how they bind to different receptors throughout the body. However, THCA works very similarly to other cannabinoids when consumed. It enters the bloodstream and bonds to cannabinoid receptors through the endocannabinoid system (more on this later). Normally, THC will bind to CB1 receptors while THCA does not fit those receptors due to its structure being slightly bigger than THC molecules. This is what leads it to not hold any of the psychoactive properties of THC.
There has not been much research or exploration done until recently to understand cannabinoid acids. This is due to them being classically considered inert cannabinoids. As time and research progress, however, we are learning that these cannabinoid acids may hold their own unique set of benefits and side effects.
In this guide, we will tackle the growing question, “THCA vs. THC: What’s the Difference?” and what this means to you as a curious explorer.

What is THC?
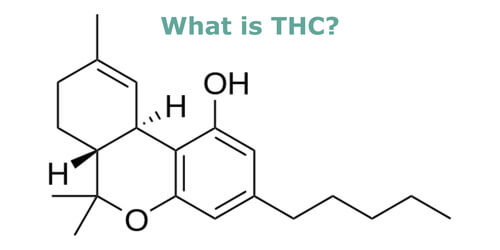
THC stands for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and is the psychoactive compound in the cannabis plant. Derived from THCA, THC is the compound that produces the “high” effect when consuming cannabis products. While found in cannabis plants, it makes a huge difference in what concentration it is found in.
Cannabis plants with a THC concentration of less than 0.3% are considered hemp plants. Conversely, cannabis plants with a THC concentration of 0.3% and above are considered marijuana plants. This affects not only the legality and where these products can be enjoyed but also what kind of experience the user has.
It should be noted that this concentration level does not influence the dosage nor does it impact the actual amount of THC consumed. How much either of these are absorbed differs greatly depending on the individual, their body makeup, and how much food or water they have consumed.
When THC does get introduced into the bloodstream, it quickly binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors with each having a different impact on the body and mind. We’ll dive deeper into the Endocannabinoid System and CB1 and CB2 receptors later on in this article.

What is THCA vs THC?
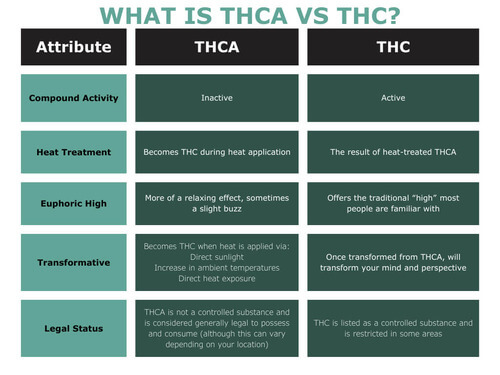
THCA vs THC differences vary both chemically and legally. Let’s take a look at some of the THCA and THC direct comparisons:
- THCA is considered an inactive compound while THC is considered to be active.
- THCA is found in freshly harvested, untreated cannabis plants. THC is made by processing THCA with heat (more details on this later).
- Consumers report that THC is what causes the “high”, euphoric feeling when consumed whereas THCA causes more of a relaxing effect.
- THCA quickly becomes THC when smoked or vaped.
- Legal status (please note, these vary from state to state):- THC is listed as a controlled substance and is restricted in some areas.
- THCA is not a controlled substance and is considered generally legal to possess and consume (although this can vary depending on your location).
The cannabis plant is full of wonder and mysteries due to its naturally occurring compounds, AKA cannabinoids. You might already be aware of one of the main cannabinoids, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, commonly known as THC.
This is what produces the “high” feeling when consuming cannabis. But did you know that in order to get THC, you must first process its precursor, THCA? Fun fact: you’re already a pro at transforming THCA into THC, read on to discover your wizardly powers!
How Does THCA Become THC?
THCA becomes THC through the application of heat. Although it’s that simple, the science behind the process is fascinating! This process is called decarboxylation. It is a chemical reaction that removes a carbon atom from a chain of carbons. Once a THCA molecule has been stripped of its carboxyl, it becomes THC. This removal makes the THC molecule more effective at bonding with various endocannabinoid receptors in the body.
This change in chemical structure is what makes THC able to bond with the CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. Because the THC molecule is smaller and better suited to the receptors, it is able to be absorbed and leads to that feeling of a euphoric “high”. So what are the different ways that this can be accomplished? This happens when raw cannabis is heated through various means by either the grower, processor, or by the consumer directly.
Here are 3 ways that THCA becomes THC:
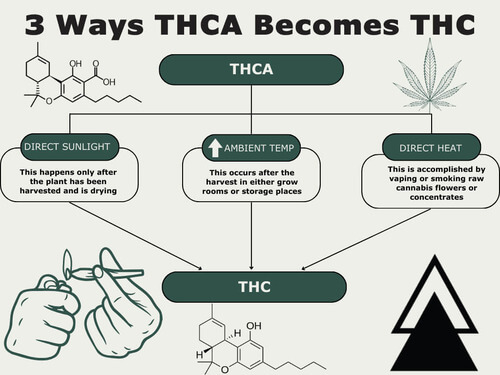
- Direct sunlight: This happens only after the plant has been harvested and is drying.
- Increase in ambient temperatures: This occurs after the harvest in either grow rooms or storage places.
- Direct heat exposure: This is the most common method that consumers are familiar with. It is accomplished by vaping or smoking raw cannabis flowers or concentrates.
 How Do You Use THCA?
How Do You Use THCA?
If you have previously used cannabis products before, most of these will feel familiar. After all, heat is the main driving force for using THCA products. That being said, here are the top 3 techniques for consuming THCA (which turns the THCA into THC):
Vaping/Dabbing: This is by far the most popular way of consuming THCA. With each puff that you take off of a THCA vape pen, the equipment converts the material into THC. This is achieved through raw flower or concentrates being heated or burned thereby delivering THC to the user. The strongest dabable form of THCA is THCA Diamonds which should be used very carefully as you learn your tolerance, even as a veteran.
- How to vape/dab THCA:- Place THCA flower or THCA wax concentrate into the heating chamber
- Activate button (or inhale depending on model) - Inhale for a few seconds then wait a few moments to gauge its effect on you
- Take 1 or 2 more puffs again waiting a few more moments to feel the effects
- Wait a few hours for desired effects to wear off before consuming more
Smoking: Also a popular consumption method, smoking THCA converts it to THC giving a strikingly similar experience to smoking THC directly. The difference is that THCA can be sold more widely than THC and it has been cared for to ensure that the THC concentration is below 0.3%.
- How to smoke THCA:- Remove a small amount from the packaging
- Grind the flower in a grinder
- Take a small amount of the flower (about a small pinch) and place it into a bong, pipe, or joint
- Apply flame to the bowl or end of the joint and inhale for a few seconds
- Take 1 or 2 more puffs again waiting a few moments to feel the effects
- Wait a few hours for desired effects to wear off before consuming more
Gummies: Since there is no heating method for consuming gummies, the THCA will not convert into THC. This means that the psychoactive effect will not be present and thus, you will not be able to get high. There are, however, user-reported benefits but it should be noted that these experiences are still being studied and no conclusive results have yet been verified. Some users have reported that THCA gummies have helped them with nausea, sleep, and anti-inflammatory effects to name a few.

Does THCA get you high?
The short answer is no. That is until you convert it to THC. In its raw form, THCA does not produce the psychoactive effects commonly associated with THC. Since the THCA cannabinoid compound is too large to fit into the endocannabinoid system receptors, it is unable to deliver the “good feeling” that we all love with THC. It does, however, hold some beneficial properties in and of itself. How you consume it will greatly affect what kind of experience you have.
How long does THCA stay in your system?
This will vary depending on your body makeup, how often and how much you consume, and of course, whether or not you have converted it into THC. Once consumed, on average, the time that it will be detectable in your system will be about 1-2 days. Detectability will also be affected by what kind of test is administered to you.
It should also be noted that consuming raw, untreated cannabis in the form of THCA will not always lead to a positive test result. Since it does not hold any psychoactive effects, it’s not something that people will test for. Please be advised however that if you do have any kind of drug screenings coming up, abstinence from consumption is the best method to ensure you do not fail a drug test.
What does THCA do to the brain?
So what does THCA do to the brain and why do people enjoy consuming it? It should be noted upfront that individual user experiences will vary and that testing and studies are still ongoing. That said, users have expressed a myriad of benefits for mental and physical health items. People have reported that consuming THCA leads to several advantages such as protecting brain health and function. There have also been claims made that it also helps with neuroinflammatory diseases such as Huntington's', Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Users have also made assertions that consuming THCA can also help with sleep issues such as insomnia and relaxation. Even further, there have been some claims that it can also help with reducing seizures and spasms in the case of epilepsy and multiple sclerosis. Again, studies and testing are still ongoing and these claims have yet to be substantiated by formal peer-reviewed processes.

The Endocannabinoid System 101
The endocannabinoid system works as an intricate messenger system responsible for maintaining balance throughout the body. Scientists have been studying these phenomena and are still learning about how it works and what benefits it can hold. Some of the more well-known body functions that are impacted by this system include appetite, sleep, stress, memory, mood, and pain management. Lesser known functions include immune system health, inflammation, skin health, and fertility.
This system was only discovered in the 1960s but we now know that it has always been a part of our anatomy and physiology. It was found that almost every last cell in the human body has receptors for cannabinoids and that they operate in a lock-and-key methodology with every individual lock system needing a particular kind of key. It was also highlighted that there are more cannabinoid receptors in the human body than any other kind of receptor. While this discovery was groundbreaking, it was not until the 1980s that scientists identified that the “key” to cannabinoid receptor “locks” were endocannabinoids themselves.
CB1 Receptors
CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system are mainly found in the central nervous system. When endocannabinoids bind to CB1 receptors, many things can happen. For example, when they bind in the spinal cord, this is seen to help with pain management and other physical ailments.
CB2 Receptors
CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system are mainly found in the peripheral nervous system. When incoming endocannabinoids bind to CB2 receptors, it is thought that this helps with immune support and health. This is believed to help with issues such as inflammation and immunity but studies are still ongoing to determine the full breadth of benefits the relationship between endocannabinoids and CB1 and CB2 receptors can have.

Is THCA legal?
Before understanding the legality and availability of cannabis products, it’s important to understand the basics of the 2018 Farm Bill. This bill helped farmers, ranchers, and forest management with issues they were facing regarding farm support, crop insurance, disaster relief programs, and conservation efforts.
Among the many, many benefits of the 2018 Farm Bill, however, is the legalization of industrial hemp. Under this bill, cannabis plants with a THC concentration of less than 0.3% are considered hemp plants and not marijuana. This allowed hemp plants to be removed from the list of controlled substances thereby opening up a huge new market for hemp growers and distributors. It should be noted that this does not apply to every single state and that there are still parts of the country where any and all cannabis products are not allowed.

THCA FAQs
What is the difference between THCA and THC?
Cannabis plants contain THC and THCA, two different chemical compounds. The psychoactive compound in marijuana is THC, while THCA is a non-psychoactive precursor to THC that must be heated to produce it. Essentially, THC will get you high while THCA will not (unless you convert it to THC via heat.)
What is THCA?
The molecule that becomes THC is tetrahydrocannabinol acid or THCA. This process is accomplished through applying various forms of heat to the raw, untreated hemp flower.
Does THCA get you high?
No, but once converted into THC, it will. This process is called decarboxylation and it removes the acid molecule (the “a” in THCA) from the flower thereby leaving behind THC, which will get you high.
What are the benefits of THCA?
THCA consumers have self-reported that it can help with issues such as mind and body health and protection. While official, conclusive studies are still underway, consumers have claimed that it can assist with things such as mood, memory, sleep, stress, and appetite. They have also stated that it may help with things like immune system health, inflammation, skin health, and fertility.
Is THCA legal federally?
No, but it has been removed from the list of controlled substances recognized by the government. The legality will vary from state to state and it is important to look first into the particulars of where you live.
Sources:
https://www.leafly.com/news/cannabis-101/what-is-thca-and-what-are-the-benefits-of-this-cannabinoid


